Path Sum II
Problem
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values in the path equals targetSum. Each path should be returned as a list of the node values, not node references.
A root-to-leaf path is a path starting from the root and ending at any leaf node. A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
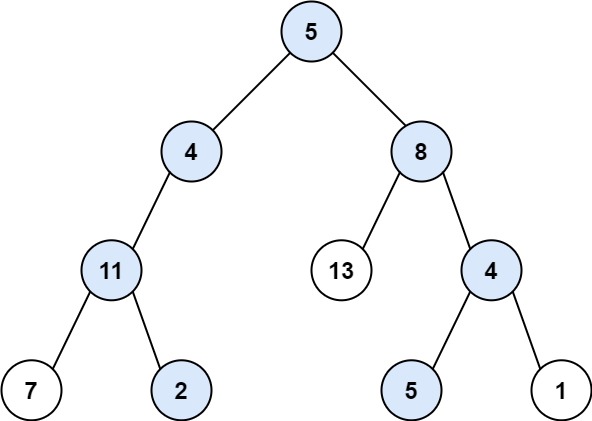
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]] Explanation: There are two paths whose sum equals targetSum: 5 + 4 + 11 + 2 = 22 5 + 8 + 4 + 5 = 22
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} targetSum
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
const res = [];
const dfs = (node, target, path) => {
if (!node) {
return;
}
const sum = target - node.val;
path.push(node.val);
if (node.left || node.right) { // it not leaf node
dfs(node.left, sum, path);
dfs(node.right, sum, path);
} else if (!sum) { // is leaf node
res.push([...path]);
}
path.pop();
}
dfs(root, targetSum, []);
return res;
};
We will implement a DFS solution. We traverse the tree root while keeping track of our path path. When we reach a leaf node, check if targetSum is 0, if so, add path to our resulting set res.